CORNEA
The cornea is a transparent layer in the front part of the eye which focuses the light and protects the eye from external agents, and thus plays an important role in the visual process. A number of diseases have a negative impact on the cornea’s transparency. They may be congenital and have genetic roots or be viral. Some diseases such as keratoconus are very serious because they change the shape of the cornea and require a cornea transplant.
FREQUENTLY SEEN CORNEA DISEASES
- Keratitis: Cornea inflammation
- Keratoconus: An advancing disease characterised by thinning and liquefaction of the cornea
- Dry eye syndrome/keratoconjunctivitis sicca: The condition of having dry eyes
- Cornea erosion: Damage due to cutting, grazing or scratching of the cornea surface.
What is Keratoconus?
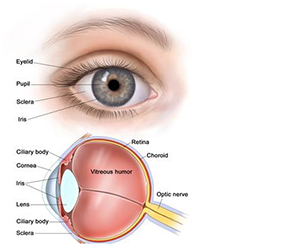
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease in which the normally round cornea thins and begins to bulge into a cone-like shape. This cone shape deflects light as it enters the eye on its way to the light-sensitive retina , causing distorted vision and is often not satisfactorily corrected with glasses. Glare and light sensitivity also may occur. Often, keratoconic patients experience changes in their eye glasses prescription every time they visit their eye doctor. The Normal Cornea The eye is like a camera in which lenses focus the picture on a light sensitive film. In the human eye, the transparent cornea and lens focus light on the retina, which changes it into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain by the optic nerve to be perceived as images.

WHAT CAUSES KERATOCONUS?
New research suggests the weakening of the corneal tissue that leads to keratoconus may be due to an imbalance of enzymes within the cornea. This imbalance makes the cornea more susceptible to oxidative damage from compounds called free radicals, causing it to weaken and bulge forward. Risk factors for oxidative damage and weakening of the cornea include a genetic predisposition, overexposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun, excessive eye rubbing and chronic eye irritation.
KERATOCONUS TREATMENT
In the mildest form of keratoconus, eyeglasses or soft contact lenses may help. But as the disease progresses and the cornea thins and becomes increasingly more irregular in shape, glasses and regular soft contact lens designs no longer provide adequate vision correction.
TREATMENTS FOR PROGRESSIVE KERATOCONUS INCLUDE:
• Corneal cross-linking (CXL)
• Custom soft contact lenses
• Gas permeable contact lenses
• “Piggybacking” contact lenses
• Hybrid contact lenses
• Scleral and semi-scleral lenses
• Intacs
• Topography-guided conductive keratoplasty
• Corneal transplant
Corneal crosslinking.
This procedure, also called corneal collagen cross-linking or CXL, strengthens corneal tissue to halt bulging of the eye’s surface in keratoconus. The aim of this treatment is to create additional chemical bonds inside the corneal stroma by means of a highly localized photo polymerization.
The indications for cross linking today are corneal ectasia the disorders such as keratoconus and pellucid marginal degeneration, iatrogenic keratectasia after refractive lamellar surgery and corneal melting that is not responding to conventional therapy.
THE PRINCIPLE OF C3R
Photo-polymerization using UV-light was found to be the most promising technique to achieve cross-links in connective tissue. Photo-polymerization is activated by means of a non-toxic and soluble photomediator and a wavelength which is absorbed strongly enough to protect deeper layers of the eye (riboflavin-UVA technique).

UV-A radiation with concomitant administration of riboflavin solution leads to physical cross linking of the corneal collagen fibers. Thus progressive corneal thinning is slowed down or even stopped and the Bio-mechanical strength of corneal tissue is improved.
THE DEVICE FOR C3R
For C3R we need riboflavin dye and a special device called cross-linker. Cross linker is a device to deliver UV-A light of specific wavelength of 365 nm , at controlled energy level of 3 mW/cm.sq.
THE C3R PROCEDURE
After removal of the corneal epithelium, riboflavin solution is instilled for 30 minutes on to the cornea. Then the corneal penetration of this is checked by establishing that the anterior chamber is slightly yellow. Pachymetry is performed to make sure that minimum corneal

thickness is maintained. UV-A radiation starts under continued administration of Riboflavin Solution. After 30 minutes of radiation treatment is finished and the patient receives post-operative treatment like after a PRK procedure. A bandage contact lens is inserted in the operated eye and the patient is administered oral and topical antibiotics, steroids, anti-inflammatory medication as well as lubricant eye drops.



